Working in a team of people who are assigned and responsible for the same kind of role can lead to many conflicts. Take an example of an enthusiastic team of coders for an instance. They are all contributing to the same project by adding new feature and thus editing the same project’s file. Even for a single person working in a big project, it gets really complicated very fast and it becomes very difficult to keep track of all the changes made so far. For a large team it is simply not feasible. This is where “
Version Control Software (VCS)” comes into the role and saves the day.
Today we will dig into the open source version control software: “
Git” and have a little insight into its design as well as its importance. In last we will cover some basic and frequently used git commands.
What is a Version Control system?
But before jumping directly into the concept of git, I would like to talk little bit about “version control” itself. Version control is basically a system which keeps track of all the records corresponding to the changes made against the set files over a period of time. It allows you to revert a set of files or even the entire project back to a certain safe state, compare changes over time, see last modified change, track back the bugs or issues and even more. VCS reduces human overhead on tracking files as it is done automatically. Thus with VCS, we can modify, experiment, implement new features in project, without fear of losing the integrity of working project.
VCS system can be mainly characterized as either centralized or distributed. In Centralized Version Control System (CVCS), there is a main server that contains the repository of all the versioned files and any client can access the files from this central place. However, this type of setup has many disadvantages. Every node is connected to same main server. Failure of the server halts the system and thus makes it impossible for anyone to collaborate or even save the versioned change done by them.
To avoid problems of CVCS, Distributed Version Control System (DVCS) was introduced. In this kind of setup, the client mirror(or clone) the full fledged snapshots of the repository to its own local system.Thus every client has full record of all changes made in the project. Even if a node fails, it will not halt the whole system as every clone has full backup of all data. Git falls under DVCS. It enables many cool feature which we will later study.
Git was created by Linus Torvalds in 2005 for development of Linux kernel along with some other developers at initial stage. Git supports most of the major operating systems including OS X, Microsoft Windows and of course Linux as well.
Diving into Git
Let us try to understand git in the detail. Git stores all the tracking data for files stored in a git repository. For turning a project in git repository, first we initialize it inside the project’s working directory and add files that needed to be tracked. Files present in this directory can be sub categorized as either being tracked or un-tracked. We can change between the two using “git add” and “git rm” respectively. Git only sees the tracked files.
According to git, the tracked files lies in three states i.e., unmodified, modified and staged. At initial stage, all the tracked files lies in unmodified state. When we make some changes(or edit) in any tracked file, it changes its state to modified state. Before committing the tracked file, we need to add the given file into the staged state. Now If we commit the staged file, the current snapshot of the contents of your work tree at current moment is created and saved. Git stores a commit object which contains a pointer to the snapshot. Every time you commit your project, it takes whole picture of all your tracked files at current moment and store reference to that snapshot. If file is unmodified, Git simply link it to its previous identical version of the snapshot it had stored. These snapshot helps in implementing concept of version control. Git thinks about its data more like a stream of snapshots. Thus we can easily check the differences (i.e., changes) between different snapshots as well as between the currently staged files and any snapshot. This help in analyzing the changes made in the new version and gives the relevant picture. Don’t worry we will later dig further on how to exactly do it.
 |
| Figure 1. The life cycle of the status of your files. [Reference] |
In git terminology, we refer to staging area as ‘index’, other two states (i.e., unmodified and modified) to be in ‘working tree’(i.e., files that you are currently working on) and all the previous snapshots created by commit command to be in ‘history’.
Now let us understand the concept of ‘branching’ which is considered to be an essential feature of VCS. Suppose you are working on a given project. Suddenly you realize you have to add a new feature (or resolve a bug) in your project. But you can not afford to risk the current progress of the project by adding experimental code which can easily mess up logic of whole project. One thing you can do is create a copy of same project at current state and make changes to it. If the changes are successful then make it the main (or master) project. However, consider the case where many people are working together adding different new features (or resolving different bugs) then multiple copies will generated and keeping track of all these copies is simply not feasible. We need a system which does not create multiple copies; were multiple people (or a single user) can take the snapshot of current state; work on it at different branch and later when they are happy with changes made; they can easily merge the changes into the main (or master) project. This is what exactly branching helps in achieving.
For getting an insight on how branching is done by git, we have to understand how git stores stream of snapshot and keep records of commit objects (i.e., metadata generated after every commit). It can be easily understood by taking help of diagram given below. Here we have a working directory. Whenever you commit the staged file (i.e., index), it is provided with an unique identification (i.e., id) number which gets generated via SHA-1 hash function. commit object (i.e., metadata about commit) gets this id number. All the commit object points to their parent node and so on. The current branch in working tree is identified by the pointer named HEAD. Main branch is identified by the pointer named MASTER. MASTER points to the last commit object in the master branch. According to this diagram, if we will generate a new commit object, it will get add after last commit object (i.e., ed489). Therefore, MASTER and HEAD will then point to this new commit object. Here if we have another branch (namely, maint), we can access it by referencing HEAD pointer to its position. If we generate new commit object in the branch ‘maint’, we will end up having two sub tree and two child nodes sharing a common parent node(i.e., a47c3). Thus our given project will progress in two different dimensions.
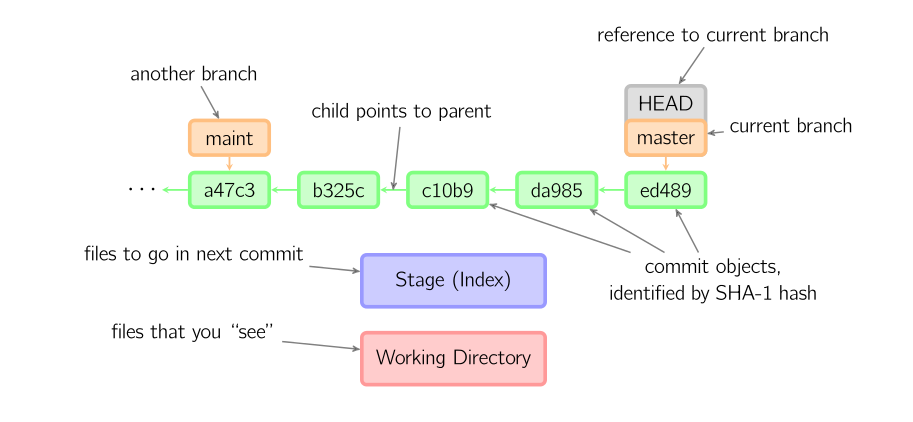 |
| Figure 2. Internal structure of git records [Reference] |
Now, after some time if we want to combine the two sub-trees into one. We can do that by using “merge” operation as shown in figure below. According to given diagram, we were present(i.e., checking-out) ‘maint’ branch and performed “merge master” operation. Merge operation creates a new merge-commit. It is used for documenting all the merges in the repository. In this diagram we have shown only simple type of merging technique which is called “fast-forward merge”. For in detail study of about git branching and merging algorithm follow this resource. [
Reference]
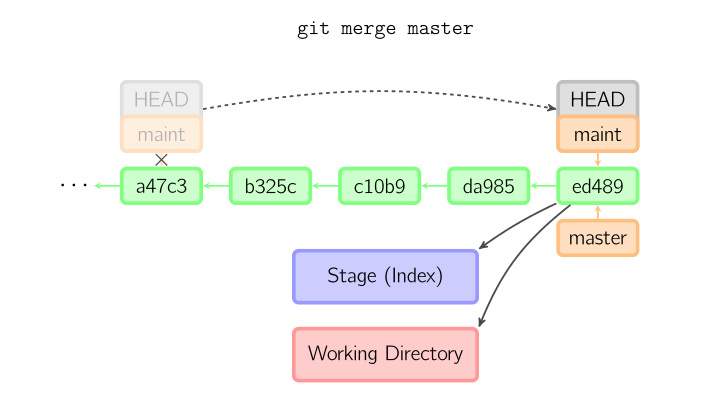 |
| Figure 3. Fast forward merge operation [Reference] |
Using Git
Now it’s time to get some hands-on git. First you must Install git and set the environment PATH for git in your operating system. [
Reference]
After installation, first thing you do is set your user_name and email_id. These fields are mandatory as git uses these information every time you commit and it is immutably backed into the commit. Any other client can view these field in log file to identify who did what commit. Thus every commit object has three main metadata its id, author_name (username and email id) and date (time-stamp when commit occurs). Now run following command in your console :
git config --global user.name "your_user_name" (enter)
git config --global user.email "your_email_id@example.com" (enter)
This will set your user name as “your_user_name” and email address as “your_email_id@example.com”. This much configuration is enough for you to get started. But for in detail configuration check out this resources. [
Reference]
Now we shall cover the basic workflow and basic commands used step by step :
1. Initialize the git repository : After you have installed git in your system. First of all go to your working directory through your console. Note that all the commands that we will discuss later in this article are to be run on the console. Now it’s time to initialize git repository in your working directory. We can do this by following command :
This will create an empty and hidden git repository or reinitialize an existing one. In this repository sub directories for head, object etc is created which helps git in tracking the progress. An initial HEAD pointer referencing master branch is also created.
2. Adding files into index : After you have initialized git repository, it is time to add files into tracked category. We can do this by following command :
git add [<file_name>] (enter)
This command can be used multiple time. It update the index by adding mentioned file from working directory. Thus it prepare staged content for the next commit which will get appended into historical snapshot. The git add command takes a path name for either a file or a directory. If it’s a directory, the command adds all the files present in that directory recursively.
3. Checking the working tree status : We can check the status of the tracked files by using following command :
Above command also tells you branch you are on.
4. Record changes to repository : Now if we want to stores the current contents of the index for the snapshot hence create a new commit object. We can do that using following command :
Above command will open your default notepad where you can type your commit message. It is not mandatory but recommended as it is useful for quick reference for what the commit object was about. For changing the editor run the following command :
git config --global core.editor “<path/to/editor>” (enter)
5. Checking changes between commits, commit and working tree : We can track the changes using running following commands :
For checking difference between your working directory and index :
For checking difference between a modified file (namely, file_name) and last committed node present in your local repository :
git diff HEAD [<file_name>] (enter)
For checking difference between staged files (i.e., index) and local repository files :
git diff --cached [<file_name>] (enter)
In output '+' represent line added and '-' represent line removed in your file.
6. Feature of branch : We can create a new branch using following command :
git branch [<branch_name>] (enter)
Above command will create a new branch namely ‘branch_name’ at current node. Now we can switch from current branch “master” (say) and to this new branch (namely, branch_name) by running following command :
git checkout [<branch_name>] (enter)
Above command will make HEAD pointer reference to this new branch thus changing the local branch. Now we can merge historical snapshot of the new branch (namely, branch_name) into the current branch (say, master) by running following command :
git merge [<branch_name>] (enter)
7. Viewing commit log : We can do this using following command :
Above command is useful for tracing back the all the commits. It is metadata of commit object which contains author name, date and commit message.
I have only covered some of the very basic commands for getting you started. There is so much you can do and it is practically impossible to cover all of them in this article. I would recommend you to check out this resource for sharpening your skills. [
Reference]
In the end, We can say git is “revision control” tool for managing your tracked file in your working directory. By far we have assumed that git repository is present in our own local system and thus can be accessed by a single user only. For team project, git repository can be hosted on remote server, and team members have their own local copy which they can modify and merge the changes back to remote. We can host the git repository in any server and there are many online platform available for hosting git repository like GitHub, GitLab, BitBucket etc.
The above code snippets are successfully tested on Mac OS X and Linux.
Other useful links:






























